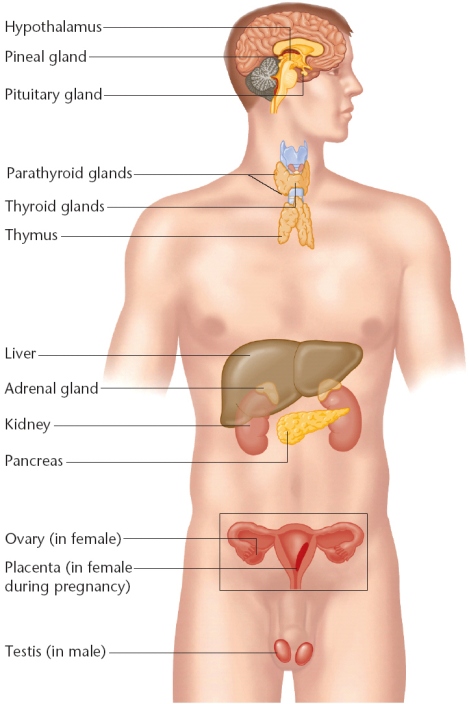
 The major glands that make up the human endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pineal body, and the reproductive glands, which include the ovaries and testes. The pancreas is also part of this hormone-secreting system, even though it is also associated with the digestive system because it also produces and secretes digestive enzymes.
The major glands that make up the human endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pineal body, and the reproductive glands, which include the ovaries and testes. The pancreas is also part of this hormone-secreting system, even though it is also associated with the digestive system because it also produces and secretes digestive enzymes.
Although the endocrine glands are the body’s main hormone producers, some non-endocrine organs — such as the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, thymus, skin, and placenta — also produce and release hormones.
A hormone (from Greek ὁρμή, “impetus”) is a chemical released by a cell, a gland, or an organ in one part of the body that affects cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one cell to another. All multicellular organisms produce hormones; plant hormonesare also called phytohormones. Hormones in animals are often transported in the blood. Cells respond to a hormone when they express a specific receptor for that hormone. The hormone binds to the receptor protein, resulting in the activation of a signal transduction mechanism that ultimately leads to cell type-specific responses.
Endocrine hormone molecules are secreted (released) directly into the bloodstream, typically into fenestrated capillaries. Hormones with paracrine function diffuse through the interstitial spaces to nearby target tissues.
A variety of exogenous chemical compounds, both natural and synthetic, have hormone-like effects on both humans and wildlife. Their interference with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body can change the homeostasis, reproduction, development, and/or behavior, just as endogenously produced hormones do.
Hormonal signaling involves the following:
- Biosynthesis of a particular hormone in a particular tissue
- Storage and secretion of the hormone
- Transport of the hormone to the target cell(s)
- Recognition of the hormone by an associated cell membrane or intracellular receptor protein
- Relay and amplification of the received hormonal signal via a signal transduction process: This then leads to a cellular response. The reaction of the target cells may then be recognized by the original hormone-producing cells, leading to a down-regulation in hormone production. This is an example of a homeostatic negative feedback loop.
- Degradation of the hormone.
Hormone cells are typically of a specialized cell type, residing within a particular endocrine gland, such as thyroid gland, ovaries, and testes. Hormones exit their cell of origin via exocytosis or another means of membrane transport. The hierarchical model is an oversimplification of the hormonal signaling process. Cellular recipients of a particular hormonal signal may be one of several cell types that reside within a number of different tissues, as is the case for insulin, which triggers a diverse range of systemic physiological effects. Different tissue types may also respond differently to the same hormonal signal. Because of this, hormonal signaling is elaborate and hard to dissect.